Econet
[Networking]
Econet
Introduction
Acorn's 1980 specification for Econet was:
- Up to 255 stations per Econet
- Econets may be joined together by Gateways
- Connection by 4-wire cable to each station (typical cost in 1980 12p per metre)
- Station seperation up to 1 Kilometre
- Data transfer rate up to 210 kilobaud
- Differential signals for high noise-immunity and minimal radiation
- Crash-detect circuitry and colision-arbitration algorithm minimise the need for retries
- Econet hardwarer fits inside Atom case; eurocard version for Acorn System 2/3/4
- Econet software in 4K ROM, fits on Atom board
- Econet executed automatically on BRK
The Econet network is totally democratic in that all stations have equal status and, unless specifically prohibited, any station may communicate with any other with recourse to an intermediary. The only unique station is the one that generates the network clock, but this may be an Atom or a larger system. On larger networks, the stations at the extreme ends are terminated, the termination circuitry is on the Econet board.
Here is a 1982 Econet network:
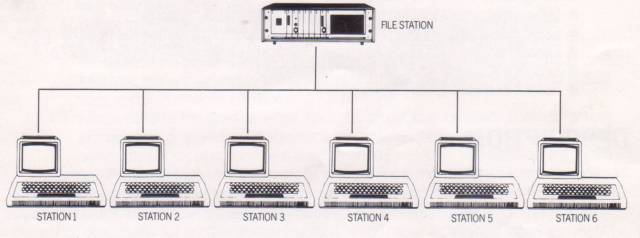
A shared disk facility is provided by a station dedicated to running a program known as the 'file server' which organises disc files for the network. The file station may be an Acorn system 3, 4 or 5 or an Atom with a disc. In the simplest possible configuration the printer station can be a printer connected to an Atom running the 'print server' program. In larger configurations the printer server will include a disc unit to spool files before printing.
Here is a 1984 Econet network:
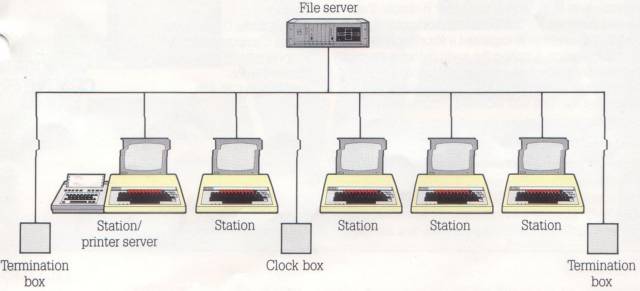
The Econet architecture evolved and in 1981, Econet had seperated the terminators and clock from the Interface cards and made them dedicated devices. Meanwhile the stations had become BBC micros with Econet interfaces, although the File server was still a System 3,4 or 5.
Here is a 1988 Econet network:
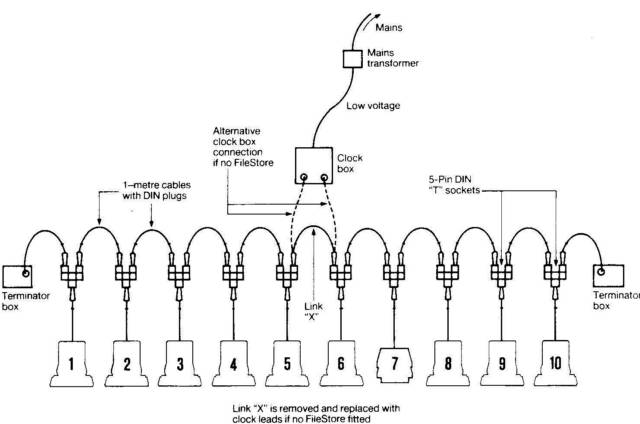
A simple, "single-room" Econet network from 1988, where station 7 is a Filestore.
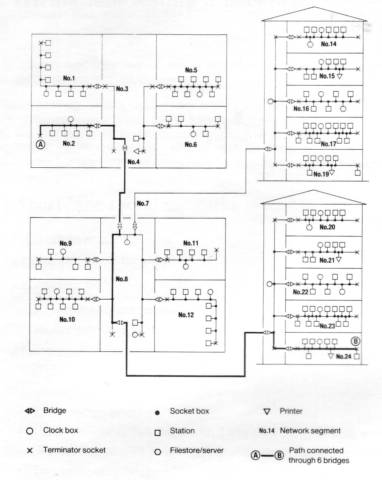
A complex Econet network from 1988, it links multiple buildings and uses bridges between them.
Documents
Here are some Acorn Econet brochures:
Here is the 1986 Acorn brochure APP81 Local Area Networking Econet .
Here is the Econet System user guide which documents the 1982 Econet system.
Here is the Econet Installation Guide which documents the 1984 Econet System.
Here is the Econet Installation Guide from 1988. The last 2 network diagrams, above, are in this manual.
Here are some additional Acorn Econet Manuals:
Econet Infrastructure
The Econet infrastructure is made up of:
- Bridges, a bridge connects one Econet network to another network.
- Clock boxes, an Econet clock sets the timing for the network and synchonises the fileserver and station Econet interfaces.
- Terminators, terminators mark either end of an Econet network and stop the signals reflecting back down the network disrupting communication.
- Socket boxes, socket boxes connect a station to the network via a flylead.
- Cables and T-pieces, a T-piece is an alternative to a socket box for small networks. Cable link the Socket boxes (or T-Pieces together forming the network and flyleads connect stations to the socket boxes or T-pieces.
- Stations, stations are computers with Econet interfaces which are connected to the network by a socket box or T-piece.
- Econet servers, are computers running server software which provide file and print services to Econet stations.
- Gateways, connect Econet networsk to other types of network.
- Transient Supressors , to protect an Econet network from external electrical activity.
Acorn produced starter packs which contained all you needed to set up a small network. It the late 1980's it was the AEH19 Econet Starter Kit and in the early 1990's it was replaced with the AEH51 Econet Starter Pack . I have an example from the early 1990s, when the supply of Econet components has been outsourced to SJ Research.
Acorn produced Econet Test Boxes to test Econet interfaces.
Bridges
I know of 2 different Econet Bridges:
Clock boxes
I know of 4 different Econet Clock Boxes, 3 from Acorn and 1 from SJ Research. A number of Acorn Econet products can also include Econet Clocks e.g. System 3, 4, or 5 Econet interfaces, Atom Econet Interface, Econet bridge, Econet Filestore E01 & E01S. Also the SJ Research MDFS and BEN contain clocks. See the individual products for details.
Terminators
Socket boxes
Socket boxes connect a station to the network via a flylead. There are both Acorn and SJ Research socket boxes.
Cables & T-Pieces
- Econet Cables and T-pieces , Cables and T pieces connect stations together. T-pieces are an alternative to socket boxes for small networks
Stations
Stations are computers with Econet interfaces connected to the network. With the BBC Master, Acorn designed an Econet module which was easy to install because it plugged into sockets on the motherboard. Acorn kept this design for all their subsequent computers up to the RiscPC, except for the A4 laptop. The RiscPC (and A7000) Econet interface plugged into the RiscPC network slot. Probably the only common Acorn computers which do not have an Econet interface are the Electron and the A3010, which were designed for home use.
All Acorn Econet interfaces use the Motorola MC68B54 advanced data link controller which controls the data transmissions.
- Acorn System 3, 4 or 5 , the Acorn Econet Node interface is a standard Eurocard to fit into the card cage of a System computer.
- Atom, I have heard of this interface, but I don't have one. [Wanted ]
- BBC Micro, the Acorn ANB22 Econet Upgrade added the Econet Interface and DFS ROM to a BBC Micro. Some models, including the US and German versions had it fitted as standard.
- BBC Master, the ADF10 Econet module was designed for the Master. This Econet module was also used in the Archimedes computers and A5000. There was also a special version, the Master ET , designed for use as an Econet terminal.
- A4, the ALA66 Econet module was designed for the A4, because of the different design of the A4 and the need to fit into the selected case.
- A3020/A4000, the AEH52 Econet module is an improved version of the ADF10 Econet module.
- RiscPC, was designed with a seperate network slot and Acorn designed the AEH60 Econet card to fit it.
- IBM-compatible PC, in 1987 Acorn produced an Econet interface for a PC, this was the AEH30 Ecolink which was a full length ISA card. It was only supported under MSDOS 3.3, so is not much use in today's PCs. [Wanted ]
Third Party Interfaces
In addition to the Acorn Econet modules, at least 3 other companies produced Econet modules for Acorn computers:
- HCCS, the HCCS Econet module is called a Network Board and was designed for Archimedes and A3000 computers.
- Oak Solutions, the ClassROM/Econet card fits in the network slot of an A3020/A4000 and allows connection to an Econet network.
- White Wing Logic, the White Wing Logic interface is called Interclock and has space for the econet clock circuitry.
Econet servers
There are 2 types of Econet servers, file servers and print servers. File servers serve files to the stations on a Econet network and, except in very early Econets, a file server has one or more hard discs. An Econet network can have one or more file servers.
Print servers support shared printers, normally a print server is a BBC Model B with the AES22 Print Server EPROM and is dedicated to printing but can double as a Econet station.
- Acorn Level 1 File Server, the Level 1 Fileserver software is on a 40 track disc (AES20) or 80 track disc (AES23) and runs on a BBC Model B or Master 128 with a floppy disc drive and Econet interface. It provides access to files stored on floppy discs and simple file transfer commands. Here is the Econet Level 1 file server user guide and the Econet Level 1 file server manager's guide
- Acorn Level 2 File Server, the Level 2 Fileserver software (AES21) is on an 80 track disc and runs on a Master Turbo, Master 128 or BBC Model B with 6502 second processor, dual 800K floppy disc drive and Econet interface. Here is the Econet Level 2 file server user guide and the Econet Level II, III and Filestore Error codes .
- Acorn Level 3 File server, The Level 3 file server software runs on a Master Turbo, Master 128 or BBC Model B with 6502 second processor, 10 MB or 30MB hard disc, dual 800K floppy disc drive and Econet interface. I have seen the Acorn Level 3 file server real time clock module auctioned on Ebay, but have no details of it. I believe it is required if you use a BBC Model B with 6502 second processor as the platform for the Level 3 file server because the BBC, unlike the Master, does not have a realtime clock.
- Acorn Level 4 File server, the Acorn Level 4 File Server was designed to run on an Archimedes Computer with an ARM2 CPU running RISC OS 2.
- Acorn Filestore E01 & E20, The Filestore E01 (AEH26) is a dedicated Econet file server with a 65C102 CPU, 64K ROM, 64K RAM, Econet clock and 2 x 3.5" floppy disc drives. The Filestore E20 (AEH27) is designed to operate connected to the E01 Expansion bus with 1 x 20MB Winchester disc drive. Here is the Acorn brochure for the Econet Filestore. I don't have either a FileStore E20. [Wanted ]
- Acorn Filestore E01S, E40S & E60S, the FileStore E01S (AEH35) is a dedicated Econet file server. The Filestore E40S (AEH36) and Filestore E60S (AEH37) are designed to connect to the E01S Expansion bus (a SCSI interface) with a 40MB (E40S) or 60MB (E60S) Winchester disc drive. The Filestore servers are stacked on top of each other. I don't have a FileStore E60S. [Wanted]
- SJ Research FDFS, the SJ Research Floppy Disc File Server (FDFS) supports the Acorn level 2 and 3 file server protocol. Its configuration is 6MHz Z80B CPU, 64K RAM, 64K cache RAM, 2 x twin double sided 80 track floppy disc drives, parallel printer channel, serial printer channel and clock. The FDFS can support more than 40 users. In 1986 an FDFSwould have cost you £986 (£800 for education users). Here is a brochure describing the SJ Research FDFS. I do not have an FDFS. [Wanted]
- SJ Research HDFS, the SJ Research Hard Disc File Server (HDFS) supports the Acorn level 2 file server protocol. Its configuration is 2 x 6MHz Z80B CPUs, 192K RAM, 256K cache RAM, upto 80MB hard disc drives, 2 parallel printer channels and clock. The HDFS automatically date and time stamps files when saved or updated and supports disc space accounting which allows disc space limits to be set for each user. The HDFS can support up to 256 user accounts. In 1986 an 80MB HDFS would have cost you £9,000 (£7,200 for education users)! Here is a brochure describing the SJ Research HDFS. .
- SJ Research MDFS, the SJ Research Modular (or Mixed) File Server supports the Acorn L2 and L3 file server protocols. The MDFS automatically date and time stamps files when saved or updated and supports disc space accounting which allows disc space limits to be set for each user. The MDFS can support up to 80 logged-on users. In 1986 an MDFS with 20MB hard disc and tape streamer would have cost you £3,600 as an educational user.
- Network Solutions Advanced Level 4 Server, the Advanced Level 4 Server is a software product designed to run on an 32bit Acorn Computer running RISC OS 3.10 or later and ran on either an Acorn AUN or SJResearch network. It is an updated version of the Acorn Level 4 server. By the time it was released in 1997 most schools were replacing Econet with Ethernet networks and using Intel based fileservers running Windows NT or Unix.
Gateways
A Gateway connects an Econet network to another network.
Transient suppressors
Transient suppressors block transient signals caused by external electrical events and protect the network. They are typically used where an Econet spans two different buildings to protect the network from external events (e.g. lightning strikes).
Test Equipment
Acorn also produced test equipment to help diagnose Econet faults.
Econet Software
While most Econet software was provided in ROM (on the client) or on the server by Acorn (or SJResearch), there were a number of thrird party Econet products. These include:
Angelsoft AppFS
AppFS is a software Application Accelerator which speeds the loading of software by client stations.
Here is Angelsoft AppFS Release 3 .
Digital Services Ltd NetGain
NetGain is a 'High Speed Application Loader'. NetGain was available for Econet or Ethernet and consisted of a Licence Card podule, end user licence packs and the software on a 3.5" disc. In use it marked reduced loading times. There is a review in Archive Vol.7 Isuue 1 (October 1993) page 77.
Here is the Digital Services NetGain Licence Card and more details of NetGain.




